This function returns variance based on the entire population, which includes numeric, logical, or text values.
VARPA(value1,value2,...)
VARPA(array)
VARPA(array1,array2,...)
Each argument can be a double-precision floating-point value, an integer value, text, a logical value, or an array (cell range) of these. Up to 255 arguments may be included. You can use a single array (cell range) instead of a list of values. You can use multiple arrays (cell ranges) as well.
The variance returns how spread out a set of data is.
Each argument can be a double-precision floating-point value, an integer value, text, a logical value, or an array (cell range) of these. Up to 255 arguments may be included. You can use a single array (cell range) instead of a list of values. You can use multiple arrays (cell ranges) as well.
This function uses the following equation to calculate the variance, where n is the number of values.
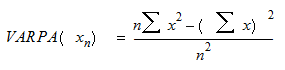
where x is the value and n is the number of values.
This function assumes that its arguments are the entire population. If your data represents only a sample of the population, then compute the variance using the VARA function.
This function differs from VARP because it accepts logical and text values as well as numeric values.
Accepts numeric, logical, and text data for all arguments. Returns numeric data.
VARPA(B3,C4,B2,D10,E5)
VARPA(A1:A9)
VARPA(R1C2,100,R2C5,102)
VARPA(98,85,76,87,92,89,90) gives the result 39.2653061224